The Impact of Digital Identity Verification on Financial Auditing is reshaping the landscape of financial control and assurance. This transformative technology offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance accuracy, mitigate risks, and streamline the audit process. From automating data validation to bolstering fraud detection, digital identity verification is revolutionizing how financial audits are conducted, impacting everything from regulatory compliance to the auditor-client relationship. This exploration delves into the multifaceted implications of this technological shift, examining both its benefits and potential challenges.
The integration of digital identity verification into financial auditing promises a future where audits are faster, more accurate, and more secure. However, challenges remain regarding data privacy, regulatory compliance across various jurisdictions, and the ethical implications of using advanced technologies for identity verification. This analysis will provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of digital identity verification in financial auditing, exploring its impact on various aspects of the field and offering insights into future trends and potential obstacles.
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency in Auditing
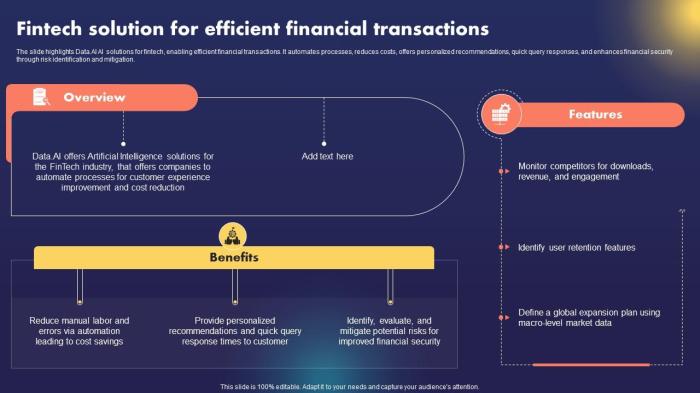
Digital identity verification is revolutionizing financial auditing, significantly improving accuracy and efficiency. By leveraging technology to confirm the identities of individuals involved in financial transactions, auditors can enhance the reliability of their findings and streamline the entire audit process. This leads to cost savings and reduced risks associated with fraudulent activities.
Digital identity verification improves the accuracy of financial data collection by eliminating the reliance on potentially unreliable manual processes. Traditional methods often involve physical document checks and manual data entry, both prone to errors and inconsistencies. Digital verification, on the other hand, uses automated systems to cross-reference data from multiple sources, providing a more comprehensive and accurate picture of a company’s financial position.
Investigate the pros of accepting How Corporate Debt Structuring Affects Financial Reports in your business strategies.
Streamlining the Audit Process
Digital identity verification significantly streamlines the audit process, reducing both the time and resources required. Automated systems can instantly verify the identities of numerous individuals, eliminating the need for lengthy manual checks. This allows auditors to focus on higher-level analysis and interpretation of financial data, rather than spending time on tedious verification tasks. For instance, verifying the identity of thousands of shareholders in a large public company can be accomplished in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. This frees up auditor time for more complex aspects of the audit, ultimately increasing overall efficiency.
Minimizing Human Error in Data Validation
Automated identity verification systems minimize human error inherent in manual data validation. Manual processes are susceptible to mistakes such as misreading documents, incorrectly entering data, or overlooking crucial details. Digital systems, however, are programmed to follow strict verification protocols, minimizing the chance of human error. For example, a system can automatically flag discrepancies between a provided ID and the company’s internal records, alerting auditors to potential issues that might otherwise be missed. This automated flagging system drastically reduces the risk of overlooking crucial information, leading to a more reliable audit.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Auditing Methods
Traditional auditing methods, relying heavily on manual processes and paper-based documentation, are significantly slower and more resource-intensive than those incorporating digital identity verification. The manual nature of these processes increases the likelihood of human error and delays in completing the audit. In contrast, digital identity verification allows for a much faster and more efficient audit process, leading to quicker turnaround times and reduced costs.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
| Method | Time Taken | Resource Consumption | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Auditing | Weeks to Months | High (personnel, travel, paper) | High (potential for human error) |
| Digital Identity Verification Integrated Auditing | Days to Weeks | Moderate (software licenses, personnel) | Low (automated verification minimizes errors) |
Risk Mitigation and Fraud Detection
Digital identity verification plays a crucial role in bolstering the security and reliability of financial audits. By strengthening the authentication process, it significantly reduces the risk of fraudulent activities and enhances the overall integrity of financial reporting. This section will explore how this technology mitigates risk and improves fraud detection capabilities.
Real-time identity checks are a cornerstone of modern fraud prevention. The immediate verification of an individual’s identity before access to sensitive financial data is granted significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access and manipulation. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, which often rely on less secure authentication mechanisms and are more vulnerable to sophisticated attacks.
Vulnerabilities Addressed by Digital Identity Verification in Traditional Auditing
Traditional auditing processes often suffer from vulnerabilities that digital identity verification directly addresses. For instance, reliance on static passwords or easily guessable usernames leaves systems open to brute-force attacks and phishing scams. Furthermore, the lack of real-time monitoring and verification allows fraudulent activities to persist undetected for extended periods. Digital identity verification, with its multi-layered authentication methods, provides a robust defense against these weaknesses. It introduces a higher barrier to entry for malicious actors, making it significantly more difficult to compromise systems and manipulate financial data.
Illustrative Scenario: Detecting Fraudulent Transactions with Digital Identity Verification, The Impact of Digital Identity Verification on Financial Auditing
Imagine a scenario where a company’s accounting system is compromised. A malicious actor attempts to initiate a large, unauthorized wire transfer. With traditional methods, this fraudulent transaction might go unnoticed until a later reconciliation. However, with digital identity verification in place, the system would immediately flag the transaction for review. The system would detect that the individual initiating the transfer does not match the verified digital identity associated with the authorized user. This immediate alert allows for swift intervention, preventing the fraudulent transaction from being completed and minimizing financial losses.
Biometric Authentication Strengthening Financial Audit Trails
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, add another layer of security to financial audit trails. These methods are incredibly difficult to replicate, making them highly effective in preventing unauthorized access and modifications. The integration of biometric data into the audit trail provides an irrefutable record of who accessed and modified specific financial information, enhancing accountability and simplifying investigations into potential fraudulent activities. For example, if a discrepancy is found in a financial report, biometric logs can quickly identify the individuals who had access to the relevant data at the time of the discrepancy, narrowing down the scope of the investigation. This significantly improves the efficiency and effectiveness of fraud detection and investigation processes.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Security
Digital identity verification (DIV) significantly impacts financial auditing by streamlining compliance with numerous regulations while bolstering data security. Its implementation offers a robust solution to the challenges posed by traditional methods, enhancing both the efficiency and trustworthiness of the auditing process. The integration of DIV directly addresses key concerns regarding data privacy and security, a critical aspect in today’s regulatory landscape.
The use of DIV facilitates compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA by providing a verifiable and auditable trail of identity verification. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and strengthens the overall security posture of financial institutions. By accurately identifying individuals involved in financial transactions, DIV allows for better monitoring of access to sensitive data and facilitates the detection of potential fraudulent activities.
Impact of Digital Identity Verification on Regulatory Compliance
Meeting regulatory compliance requirements for financial audits is significantly simplified through the implementation of DIV. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States mandate robust identity verification and data protection measures. DIV provides an auditable record of identity verification, simplifying compliance audits and demonstrating adherence to these regulations. This reduces the risk of non-compliance fines and reputational damage. For example, a financial institution using DIV can readily demonstrate to auditors that only authorized personnel accessed sensitive client data, satisfying GDPR’s data access control requirements. Similarly, under CCPA, the clear audit trail provided by DIV aids in fulfilling requests for data access and deletion.
Contribution of Digital Identity Verification to Sensitive Financial Data Protection
Digital identity verification plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive financial data. By confirming the identity of individuals accessing or handling financial information, DIV reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), a common component of DIV, adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly more difficult for malicious actors to gain access. Moreover, DIV enables granular access control, limiting access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel based on their verified identity and role within the organization. This significantly minimizes the potential impact of insider threats and external attacks. The use of encryption and secure data storage further enhances the protection offered by DIV, ensuring that even if a breach occurs, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Comparison of Digital Identity Verification Methods and Regulatory Compliance
Different DIV methods offer varying levels of compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Knowledge-based authentication (KBA), while relatively simple, might not meet the stringent requirements of GDPR regarding data minimization and purpose limitation. On the other hand, methods employing biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, offer a higher level of security and often align better with regulatory requirements, provided appropriate data protection measures are in place. However, biometric data processing necessitates strict adherence to data privacy regulations, requiring robust consent mechanisms and secure storage practices. The use of government-issued IDs, coupled with secure verification processes, typically offers strong compliance with most regulations. The selection of the most appropriate method depends on the specific regulatory environment and the sensitivity of the data being protected.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy and Security with Digital Identity Verification in Auditing
Implementing robust data privacy and security measures is crucial when using DIV in auditing. This includes obtaining explicit consent for data processing, adhering to data minimization principles, and implementing strong access control mechanisms. Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is paramount, protecting data from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Furthermore, regular employee training on data privacy and security best practices is essential to mitigate the risk of human error. Finally, maintaining detailed audit logs of all DIV activities is crucial for accountability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Improved Security Posture of Financial Institutions through Digital Identity Verification
Implementing DIV significantly improves the overall security posture of financial institutions during audits. By reducing the risk of unauthorized access, identity theft, and fraud, DIV strengthens the institution’s defenses against cyberattacks and strengthens its overall compliance with regulatory requirements. The enhanced security offered by DIV translates into reduced financial losses, improved customer trust, and a stronger reputation within the industry. The verifiable audit trail provided by DIV facilitates easier and more efficient audits, minimizing disruption to the institution’s operations. This ultimately leads to increased operational efficiency and cost savings.
Impact on the Auditor-Client Relationship
Digital identity verification (DIV) is revolutionizing the auditor-client relationship, fostering greater trust, transparency, and efficiency in the audit process. The shift from traditional methods to digital verification significantly alters the dynamics of interaction and collaboration between auditors and their clients.
The integration of DIV streamlines communication and enhances the overall audit experience. This leads to a more collaborative and less adversarial relationship, benefiting both parties involved. The enhanced transparency offered by DIV directly impacts the level of trust between auditors and clients.
Trust and Transparency in Audits
Digital identity verification directly improves trust and transparency. With DIV, the verification of client identities and the authenticity of documents is automated and verifiable, reducing the potential for manipulation or fraud. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, where reliance on paper-based documentation and manual verification processes leaves room for human error and potential misrepresentation. The increased transparency provided by a verifiable digital audit trail reduces uncertainty and fosters a more collaborative relationship. For instance, a client can easily verify the auditor’s identity and access audit progress reports in real-time, leading to a higher level of confidence in the process. This enhanced transparency minimizes misunderstandings and disagreements, strengthening the auditor-client relationship.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
DIV facilitates seamless communication and collaboration. Secure platforms enabled by DIV allow for the efficient exchange of information and documents, reducing delays and improving overall communication. Auditors and clients can access a shared, secure space to discuss audit findings, resolve queries, and track progress. This improves response times and enhances overall efficiency, leading to a smoother and more productive audit experience. For example, a real-time chat function within the DIV platform allows for immediate clarification of questions, preventing delays caused by traditional email exchanges. This immediate feedback loop fosters a more collaborative and responsive relationship between the auditor and client.
Scenario Illustrating Positive Impact
Imagine a mid-sized manufacturing company undergoing its annual audit. Using DIV, the company’s financial controller securely shares all relevant financial data with the auditors through a dedicated, encrypted platform. The auditors can verify the authenticity of the data and the identity of the controller instantaneously. Throughout the audit, both parties can communicate and share documents securely and efficiently through the platform. The transparency and speed of this process significantly reduce the audit time and the potential for misunderstandings. The client feels more in control and confident in the audit process, while the auditors gain increased assurance and efficiency. This collaborative approach, facilitated by DIV, results in a strengthened and more positive auditor-client relationship.
Examples of DIV Fostering Efficient and Transparent Audits
Several real-world examples showcase the benefits of DIV. Large accounting firms are increasingly adopting DIV technologies to verify client identities and access financial records. This has resulted in significant time savings and improved accuracy in audits. Furthermore, regulatory bodies are encouraging the adoption of DIV to enhance the integrity and security of financial reporting. These regulatory incentives drive further adoption and solidify the positive impact of DIV on the auditor-client relationship. The resulting increased transparency and efficiency translate into stronger client trust and satisfaction, ultimately benefiting both the auditor and the client.
Future Trends and Challenges

The integration of digital identity verification (DIV) in financial auditing is rapidly evolving, presenting both exciting opportunities and significant hurdles. Forecasting the future requires considering technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the evolving ethical landscape surrounding data privacy and security. Understanding these factors is crucial for auditors and organizations alike to navigate the transition effectively and responsibly.
Future Trends in Digital Identity Verification
The future of DIV in financial auditing points towards a more seamless, secure, and automated process. We can expect to see increased adoption of advanced biometric technologies, such as facial recognition and voice authentication, coupled with sophisticated AI-driven risk assessment tools. This will allow for faster and more accurate verification of identities, reducing manual effort and improving overall efficiency. For instance, imagine a scenario where a system automatically verifies the identity of a key stakeholder during a remote audit, minimizing delays and enhancing the overall security of the process. This trend also anticipates a move toward decentralized identity solutions, leveraging blockchain technology to create more secure and transparent systems. The use of AI-powered anomaly detection systems will further enhance the ability to identify fraudulent activities and potential risks during the verification process.
Challenges and Limitations of Widespread Adoption
Despite its potential, widespread adoption of DIV in auditing faces several challenges. One major hurdle is the need for robust data privacy and security measures. The sensitive nature of financial data requires stringent protection against breaches and unauthorized access. Another challenge is the potential for bias and discrimination in AI-driven verification systems. If not carefully designed and implemented, these systems could inadvertently perpetuate existing societal biases. Furthermore, ensuring interoperability between different DIV systems remains a significant obstacle. The lack of standardization across various platforms could hinder seamless data exchange and integration. Finally, the cost of implementing and maintaining advanced DIV technologies can be substantial, potentially posing a barrier for smaller auditing firms.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Digital Identity Verification
The use of DIV in financial auditing raises important ethical considerations. Transparency and accountability are paramount. Auditors must be clear about how DIV technologies are being used and ensure that the process is fair and equitable. Data privacy is another crucial concern. Auditors must comply with all relevant data protection regulations and take appropriate measures to protect the privacy of individuals whose identities are being verified. Furthermore, the potential for misuse of DIV technology needs to be addressed. Robust safeguards must be in place to prevent the technology from being used for discriminatory or unethical purposes. Consider, for example, the ethical implications of using facial recognition technology without explicit consent, potentially leading to violations of individual rights.
Necessary Technological Advancements
Several technological advancements are necessary to fully realize the potential of DIV in financial auditing. Improvements in biometric authentication technology are crucial for enhancing accuracy and security. The development of more sophisticated AI algorithms for fraud detection and risk assessment is also essential. Furthermore, advances in blockchain technology can facilitate the creation of more secure and transparent identity management systems. Finally, the development of standardized interfaces and protocols is necessary to ensure interoperability between different DIV systems. For instance, the creation of a universal digital identity standard, similar to how credit card payment systems operate, would greatly enhance the efficiency and reliability of the process. Such advancements would not only improve the speed and accuracy of audits but also create a more robust and trustworthy financial system.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like blockchain and AI are poised to significantly impact the future of DIV in auditing. Blockchain technology can create secure and tamper-proof records of identity verification events, enhancing audit trails and improving transparency. AI can automate various aspects of the verification process, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. For example, AI-powered systems can analyze large datasets to identify patterns of fraudulent activity, enabling proactive risk mitigation. The integration of these technologies will likely lead to a more robust, secure, and efficient audit process, significantly enhancing the overall reliability and integrity of financial reporting. The combination of blockchain’s immutability and AI’s analytical capabilities represents a powerful synergy for revolutionizing digital identity verification in financial auditing.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, the implementation of digital identity verification in financial auditing presents a significant advancement in the field. While challenges related to data privacy, regulatory compliance, and technological limitations exist, the potential benefits in terms of enhanced accuracy, fraud detection, and efficiency are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and integrated solutions, leading to a future where audits are more robust, transparent, and trustworthy. The ongoing dialogue surrounding ethical considerations and responsible implementation will be crucial to harnessing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Answers to Common Questions: The Impact Of Digital Identity Verification On Financial Auditing
What are the potential downsides of using digital identity verification in auditing?
Potential downsides include the risk of data breaches, the need for robust cybersecurity measures, and the potential for bias in algorithms used for verification. Furthermore, ensuring universal accessibility and addressing digital literacy disparities are important considerations.
How does digital identity verification affect the cost of auditing?
While initial investment in technology might be higher, long-term cost savings can be achieved through increased efficiency, reduced manual labor, and minimized errors. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on factors such as the scale of the audit and the specific technology implemented.
What types of digital identity verification methods are commonly used in financial auditing?
Common methods include knowledge-based authentication (using personal information), multi-factor authentication (combining multiple verification methods), biometric authentication (using fingerprints, facial recognition, etc.), and digital signatures.