How to Manage a Business Budget Effectively is crucial for any business’s success. Understanding your financial landscape, from tracking expenses to forecasting future revenue, is paramount. This guide provides a comprehensive approach, exploring various budgeting methods, cost-control strategies, and the importance of regular monitoring and adjustments. We’ll delve into practical techniques and tools to help you navigate the complexities of financial management and make informed decisions to ensure your business thrives.
From creating a comprehensive financial statement to utilizing budgeting software and negotiating favorable supplier deals, we’ll cover essential steps for building a robust financial foundation. We also explore the value of seeking professional advice when needed and visualizing financial data for clearer understanding and effective communication with stakeholders.
Understanding Your Business Finances: How To Manage A Business Budget Effectively
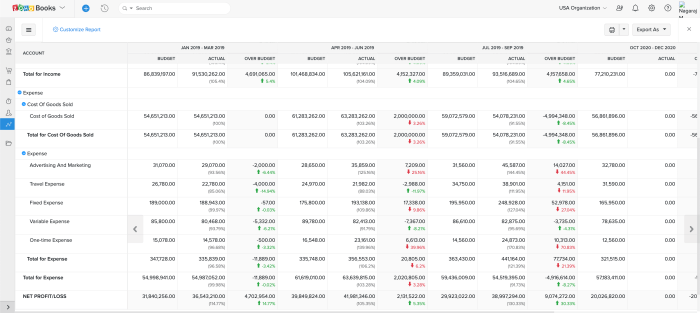
Effective budget management hinges on a thorough understanding of your business’s financial health. Accurate financial record-keeping is the cornerstone of this understanding, providing the data needed for informed decision-making and strategic planning. Without it, budgeting becomes a guesswork exercise, potentially leading to financial instability.
Accurate Financial Record-Keeping
Maintaining precise financial records is crucial for accurate budget management. This involves meticulously tracking all income and expenses, using a consistent accounting method (cash or accrual), and storing this information securely and accessibly. This data forms the basis for creating your budget, monitoring its performance, and making necessary adjustments. Inconsistent or inaccurate record-keeping can lead to inaccurate budget projections, missed deadlines for payments, and an overall lack of financial control. Regularly reconciling bank statements with your internal records helps identify and rectify discrepancies promptly.
Categorizing Business Expenses, How to Manage a Business Budget Effectively
Understanding the different types of business expenses and categorizing them effectively is essential for budgeting. This allows for better analysis of spending patterns and identification of areas for potential cost savings. Common expense categories include: Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), representing direct costs associated with producing goods or services; Operating Expenses, covering day-to-day business costs such as rent, utilities, and salaries; Marketing and Advertising expenses, encompassing costs associated with promoting your business; Research and Development, if applicable; and Administrative Expenses, encompassing general office expenses and management salaries. Categorizing expenses enables you to track spending within each area, allowing for more targeted budget adjustments.
Creating a Comprehensive Financial Statement
A comprehensive financial statement provides a snapshot of your business’s financial position. Creating one involves several steps:
- Gather Financial Data: Collect all relevant financial documents, including bank statements, invoices, receipts, and payroll records.
- Prepare an Income Statement: This statement shows your revenue, expenses, and resulting profit or loss over a specific period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). It follows the basic formula:
Revenue – Expenses = Net Income (or Net Loss)
- Prepare a Balance Sheet: This statement shows your business’s assets (what you own), liabilities (what you owe), and equity (the owner’s stake) at a specific point in time. It follows the basic accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Prepare a Cash Flow Statement: This statement tracks the movement of cash into and out of your business over a specific period. It shows how cash is generated and used, providing insights into liquidity and solvency.
- Analyze the Statements: Review the statements to identify trends, areas of strength and weakness, and potential areas for improvement.
Revenue, Expenses, and Profit Relationship
The relationship between revenue, expenses, and profit can be illustrated with a simple chart:
Imagine a bar chart. The first bar represents Revenue (e.g., $100,000). The second bar, stacked on top of the first, but in a different color, represents Expenses (e.g., $60,000). The remaining portion of the first bar, representing the difference between Revenue and Expenses, is Profit (e.g., $40,000). This visual representation clearly demonstrates how profit is derived by subtracting expenses from revenue. A larger expense bar compared to the revenue bar indicates a net loss.
Budgeting Methods and Techniques
Effective budgeting is crucial for business success. Choosing the right budgeting method and employing accurate forecasting techniques are key to financial stability and growth. This section will explore various budgeting approaches, best practices for financial projections, and the benefits of utilizing budgeting software.
Budgeting Method Comparisons
Several budgeting methods exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Zero-based budgeting, incremental budgeting, and value-based budgeting are three commonly used approaches. Zero-based budgeting starts from scratch each year, requiring justification for every expense. Incremental budgeting, in contrast, uses the previous year’s budget as a base, adjusting for anticipated changes. Value-based budgeting prioritizes expenses based on their contribution to the company’s strategic goals. Zero-based budgeting offers greater control and efficiency but requires significant time and effort. Incremental budgeting is simpler and faster but may perpetuate inefficient spending. Value-based budgeting aligns spending with strategic priorities but requires a clear understanding of value drivers.
Revenue and Expense Forecasting Best Practices
Accurate forecasting is paramount for effective budgeting. This involves analyzing historical data, considering market trends, and incorporating industry benchmarks. For revenue forecasting, consider factors like sales growth rates, market share, pricing strategies, and seasonal variations. For expense forecasting, examine historical spending patterns, planned investments, and potential cost-saving measures. Regularly reviewing and adjusting forecasts based on actual performance is essential. For example, a company experiencing unexpectedly high demand might revise its revenue forecast upwards, while one facing increased material costs would adjust its expense forecast accordingly.
Utilizing Budgeting Software and Tools
Budgeting software streamlines the budgeting process, automating tasks such as data entry, report generation, and scenario planning. Features such as real-time dashboards, collaborative tools, and forecasting models enhance efficiency and accuracy. Many software options cater to different business sizes and needs, offering varying levels of functionality and integration with other business systems.
Budgeting Software Comparison
| Software | Pros | Cons | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software A (Example: Xero) | User-friendly interface, robust reporting features, good integration with other tools. | Limited advanced forecasting capabilities, can be expensive for small businesses. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing. |
| Software B (Example: QuickBooks) | Widely used, extensive features, strong customer support. | Can be complex for beginners, some features may be redundant for smaller businesses. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing. |
| Software C (Example: Zoho Books) | Affordable, good for small businesses, cloud-based accessibility. | Fewer advanced features compared to larger solutions, integration capabilities might be limited. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing. |
| Software D (Example: FreshBooks) | Intuitive interface, excellent invoicing features, designed for freelancers and small businesses. | Limited scalability, may not be suitable for larger enterprises. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing. |
Cost Control and Expense Management
Effective cost control and expense management are crucial for business success. By strategically managing expenses, businesses can improve profitability, enhance financial stability, and free up resources for growth and innovation. This section will explore key strategies for identifying cost-saving opportunities and implementing effective expense management techniques.
Common Areas for Cost Savings
Many businesses unknowingly incur unnecessary expenses. A thorough review of operational costs can reveal significant areas for improvement. Common areas where cost savings are often achievable include office supplies, marketing and advertising, travel and entertainment, and utilities. For example, a small business might find significant savings by switching to a more cost-effective phone plan, negotiating better rates with their internet provider, or implementing a more efficient system for managing office supplies. Similarly, marketing budgets can be optimized by focusing on high-return channels and leveraging digital marketing tools effectively.
Strategies for Negotiating Better Supplier Deals
Negotiating favorable terms with suppliers and vendors is a powerful tool for cost reduction. Effective negotiation involves thorough research, preparation, and a clear understanding of your needs and the market. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to preferential pricing and extended payment terms. For instance, a business could negotiate bulk discounts by committing to a larger order volume, or explore alternative suppliers to leverage competitive bidding. Always have a clear understanding of your budget and desired outcomes before entering negotiations.
Effective Cost-Cutting Measures
Implementing cost-cutting measures doesn’t necessarily mean compromising quality. Often, small changes can yield substantial savings without impacting the overall quality of goods or services. For example, optimizing energy consumption through improved building insulation or switching to energy-efficient equipment can significantly reduce utility bills. Similarly, streamlining internal processes, automating tasks where possible, and improving employee efficiency can lead to significant cost reductions. Implementing a robust inventory management system can also minimize waste and reduce storage costs.
Actionable Steps to Reduce Operational Expenses
To effectively reduce operational expenses, businesses should take a systematic approach. This involves conducting a thorough review of all expenses, identifying areas for potential savings, and implementing targeted cost-cutting measures.
- Conduct a comprehensive expense audit: Analyze all expenses to identify areas of overspending or unnecessary costs.
- Negotiate better rates with suppliers: Leverage your purchasing power to negotiate discounts and favorable terms.
- Implement energy-efficient practices: Reduce energy consumption through improved insulation, energy-efficient equipment, and responsible usage.
- Streamline internal processes: Identify and eliminate redundant or inefficient processes to improve productivity and reduce costs.
- Automate tasks: Leverage technology to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up employee time and reducing labor costs.
- Implement a robust inventory management system: Minimize waste, reduce storage costs, and optimize inventory levels.
- Explore alternative suppliers: Compare prices and services from multiple suppliers to secure the best deals.
- Regularly review and adjust the budget: Monitor expenses closely and make adjustments as needed to stay within budget.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Budget

Effective budget management isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process requiring consistent monitoring and adaptation. Regularly reviewing your financial performance against your budget allows you to identify potential problems early, make necessary adjustments, and ultimately improve your business’s financial health. Ignoring this crucial step can lead to unforeseen financial difficulties and hinder your business’s growth.
Regular budget monitoring and analysis provides valuable insights into your business’s financial performance, enabling proactive decision-making. By tracking income and expenses against your projected figures, you gain a clear understanding of where your business stands financially. This information is essential for identifying areas where you’re exceeding expectations and areas requiring immediate attention. This proactive approach minimizes risks and maximizes opportunities for profitability.
Tracking Income and Expenses
Tracking income and expenses against the budget involves a systematic approach to recording all financial transactions. This typically includes using accounting software or spreadsheets to meticulously log all revenue streams and expenditures. Comparing these recorded figures to your budgeted amounts reveals variances, highlighting areas where you’re overspending or underspending. For example, if your budgeted marketing expense was $5,000 for the month, but you actually spent $6,000, you have a $1,000 unfavorable variance. Conversely, if you only spent $4,000, you have a $1,000 favorable variance. Regularly comparing these figures, perhaps weekly or monthly, is crucial for early detection of any issues.
Identifying and Addressing Budget Variances
Budget variances, the differences between actual and budgeted figures, should be investigated thoroughly. Understanding the reasons behind these variances is key to effective corrective action. For instance, a significant unfavorable variance in marketing expenses might indicate a need to review your marketing strategy and optimize spending. Conversely, a favorable variance in sales revenue could suggest the success of a new product launch or marketing campaign, offering valuable insights for future planning. Analyzing variances helps you pinpoint areas for improvement, refine your forecasting, and ultimately make more informed financial decisions.
Adapting to Unexpected Changes
Businesses operate in dynamic environments. Unexpected events, such as economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or changes in customer demand, can significantly impact your budget. Adapting to these changes requires flexibility and proactive adjustments to your budget. For example, if a key supplier increases their prices unexpectedly, you may need to explore alternative suppliers or adjust your pricing strategy. Similarly, a decrease in sales revenue might necessitate a temporary reduction in non-essential expenses. Regularly reviewing your budget and incorporating contingency plans for unforeseen events is crucial for maintaining financial stability during periods of uncertainty. A well-defined contingency plan, perhaps including a reserve fund, can mitigate the impact of unexpected changes. For instance, setting aside 10% of monthly profits for unforeseen expenses could provide a buffer during unexpected market fluctuations.
Financial Forecasting and Planning
Effective financial forecasting and planning are crucial for business success. It allows businesses to anticipate future financial needs, make informed decisions, and proactively adapt to changing market conditions. By projecting revenue and expenses, setting realistic goals, and tracking key performance indicators, businesses can navigate financial challenges and achieve sustainable growth.
Designing a Simple Financial Model for Projecting Future Revenue and Expenses
A simple financial model typically involves projecting revenue based on historical data, sales forecasts, and market trends. Expense projections should consider fixed costs (rent, salaries) and variable costs (materials, utilities) which often scale with revenue. A basic model might use a spreadsheet to track these figures month-by-month or quarterly, incorporating assumptions about growth rates and potential fluctuations. For example, a small bakery might project revenue based on past sales data, adjusting for seasonal variations and planned marketing campaigns. They would then estimate expenses based on ingredient costs (variable), rent (fixed), and employee wages (fixed). The difference between projected revenue and expenses represents the projected profit or loss. More sophisticated models can incorporate more complex factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and potential economic downturns. The key is to use readily available data and make reasonable assumptions.
The Importance of Setting Realistic Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is paramount for effective financial planning. Unrealistic goals can lead to frustration, demotivation, and ultimately, failure. Realistic goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They should align with the business’s overall strategic objectives and be based on a thorough analysis of market conditions, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities. For instance, aiming for a 50% increase in revenue within the first year might be unrealistic for a new startup, while a 10% increase, supported by a solid marketing plan and sales projections, could be more achievable and motivating.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track Financial Health
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) can be used to monitor a business’s financial health. These provide a snapshot of the business’s performance and highlight areas needing attention.
- Gross Profit Margin: (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue. This indicates the profitability of sales after deducting direct costs.
- Net Profit Margin: Net Profit / Revenue. This shows the overall profitability after all expenses are deducted.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Net Profit / Total Investment. This measures the efficiency of investments.
- Current Ratio: Current Assets / Current Liabilities. This assesses the ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Total Debt / Total Equity. This indicates the reliance on debt financing.
Regularly tracking these KPIs provides valuable insights into financial performance, allowing for timely adjustments to the business strategy.
Developing a Long-Term Financial Plan
A well-defined long-term financial plan provides a roadmap for sustainable growth. Developing such a plan involves several key steps:
- Define Long-Term Goals: Clearly articulate the business’s financial objectives over a 3-5 year (or longer) horizon.
- Conduct Market Research: Analyze market trends, competitive landscape, and potential risks and opportunities.
- Develop Financial Projections: Create detailed financial forecasts for revenue, expenses, and cash flow over the planning period.
- Secure Funding: Identify and secure necessary funding to support the long-term plan, considering options like loans, investments, or bootstrapping.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Select relevant KPIs to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Periodically review the plan, comparing actual results to projections and making necessary adjustments based on changing circumstances.
Seeking Professional Advice
Navigating the complexities of business finances can be challenging, even for experienced entrepreneurs. While understanding budgeting principles is crucial, seeking expert guidance can significantly enhance your financial management and lead to better outcomes. Leveraging the expertise of financial professionals provides valuable insights and support, helping you make informed decisions and optimize your business’s financial health.
Professional financial advisors and accountants offer a wealth of knowledge and experience that can significantly benefit your business. Their expertise extends beyond basic bookkeeping; they can provide strategic advice tailored to your specific business needs, helping you avoid costly mistakes and achieve your financial goals more efficiently.
Benefits of Consulting Financial Professionals
Engaging a financial professional offers several key advantages. They provide objective analysis of your financial situation, identify potential risks and opportunities, and offer tailored strategies for improvement. This expert perspective can be invaluable in making crucial decisions regarding investments, financing, and overall financial planning. Furthermore, their knowledge of tax laws and regulations can help you minimize your tax liability and ensure compliance. This can translate to significant cost savings and peace of mind.
Situations Requiring Professional Financial Assistance
Several situations necessitate seeking professional financial assistance. Rapid business growth often requires sophisticated financial management strategies that extend beyond basic budgeting. Similarly, navigating complex financial transactions, such as securing loans or investments, benefits from expert guidance. During periods of financial instability or economic downturn, professional advice is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate risk and maintain financial stability. Finally, preparing for significant business transitions, such as mergers, acquisitions, or sales, requires the expertise of financial professionals to ensure a smooth and financially sound process.
Resources for Finding Reputable Financial Professionals
Finding a trustworthy financial professional is crucial. Start by seeking recommendations from trusted sources such as other business owners, mentors, or industry associations. Online resources, such as professional directories and review platforms, can also provide valuable information. Verify credentials and experience, checking for relevant certifications and licenses. Consider scheduling initial consultations with several professionals to assess their expertise and compatibility with your business needs. Remember to thoroughly review any contracts or agreements before engaging their services.
Services Offered by Financial Advisors Relevant to Budget Management
Financial advisors offer a range of services directly relevant to effective budget management. These services typically include budget preparation and analysis, identifying areas for cost reduction, developing financial forecasting models, and providing advice on investment strategies. They can assist with cash flow management, helping you optimize your working capital and ensure sufficient liquidity. Moreover, they can offer guidance on securing financing and managing debt effectively. They can also help you establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track your progress and make data-driven decisions. For example, they might suggest tracking metrics such as net profit margin, return on assets (ROA), and debt-to-equity ratio to gauge the overall financial health and efficiency of your business.
Visualizing Financial Data
Effective visualization is crucial for understanding and communicating complex financial data. Transforming numbers into easily digestible charts and graphs allows for quicker identification of trends, anomalies, and areas needing attention, ultimately improving decision-making. This section explores methods for creating compelling visuals to represent your business’s financial health.
Creating Visually Appealing Charts and Graphs
Clear and concise visualizations are key to effective communication. Choose chart types appropriate to the data; avoid overly complex designs that obscure the message. Maintain consistency in formatting, using a consistent color palette and clear labeling. High-quality visuals, whether hand-drawn or digitally created, should be professional in appearance, reflecting the seriousness of the financial data. Consider using readily available software such as spreadsheet programs (like Excel or Google Sheets) or specialized business intelligence tools to create your charts and graphs. These tools offer a variety of chart types and formatting options to help you create professional-looking visuals.
Effective Data Visualization Techniques for Budget Reporting
Several techniques excel at illustrating budget information. Bar charts effectively compare revenue and expenses over time. Pie charts clearly show the proportion of expenses across different categories. Line graphs illustrate trends in revenue or expenses over a longer period. For example, a line graph showing monthly revenue over a year can quickly highlight seasonal variations or growth patterns. Similarly, a pie chart depicting expense categories could instantly reveal areas of overspending. Combining several chart types within a single report can provide a comprehensive overview of financial performance.
Communicating Financial Information to Stakeholders
Visual aids are invaluable when presenting financial information to stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and board members. A well-designed presentation, incorporating clear and concise charts and graphs, makes complex financial data accessible and understandable. This facilitates informed decision-making and builds confidence in your business’s financial management. For example, a bar chart comparing projected versus actual revenue for the year can quickly demonstrate the accuracy of financial forecasting. Furthermore, using consistent visuals across multiple reports ensures a unified and professional image.
Bar Chart Illustrating Monthly Revenue and Expenses
Imagine a bar chart with months of the year along the horizontal axis (January to December). The vertical axis represents monetary value in dollars. Two sets of bars are displayed for each month: one representing revenue (in blue, for instance) and the other representing expenses (in red). Taller blue bars indicate higher revenue, while taller red bars show higher expenses. Months with significantly taller red bars than blue bars highlight periods of net loss, while the opposite indicates profit. Clear labels for each bar and the axes ensure easy understanding. A legend clearly identifies revenue and expenses. This visual representation quickly communicates monthly financial performance, allowing for immediate identification of profitable and unprofitable periods. The chart could also include a line graph overlay showing the cumulative profit or loss over the year.
End of Discussion
Effectively managing a business budget is an ongoing process requiring diligence and strategic planning. By understanding your finances, implementing appropriate budgeting methods, controlling costs, and regularly monitoring your progress, you can significantly improve your business’s financial health. Remember that seeking professional advice when needed is a sign of smart business management, not weakness. With a proactive and informed approach, you can build a financially secure and prosperous future for your enterprise.
FAQ Compilation
What if my business experiences unexpected expenses?
Having a contingency fund is vital. Regularly review and adjust your budget to accommodate unforeseen circumstances. Prioritize essential expenses and explore options for cost reduction in non-critical areas.
How often should I review my budget?
Ideally, a monthly review is recommended. This allows for timely identification of variances and adjustments to maintain financial stability. More frequent reviews might be necessary during periods of significant change or uncertainty.
What are some key performance indicators (KPIs) to track?
Key KPIs include net profit margin, revenue growth, operating expenses as a percentage of revenue, and cash flow. Choosing the right KPIs depends on your specific business goals and industry.
What are the signs I need professional financial help?
Signs include consistent budget deficits, difficulty understanding financial statements, rapid business growth requiring complex financial strategies, or facing significant financial challenges like debt management.
For descriptions on additional topics like How to Register for an EIN (Employer Identification Number), please visit the available How to Register for an EIN (Employer Identification Number).